Understanding Sleep Apnea and Its Effects on Health
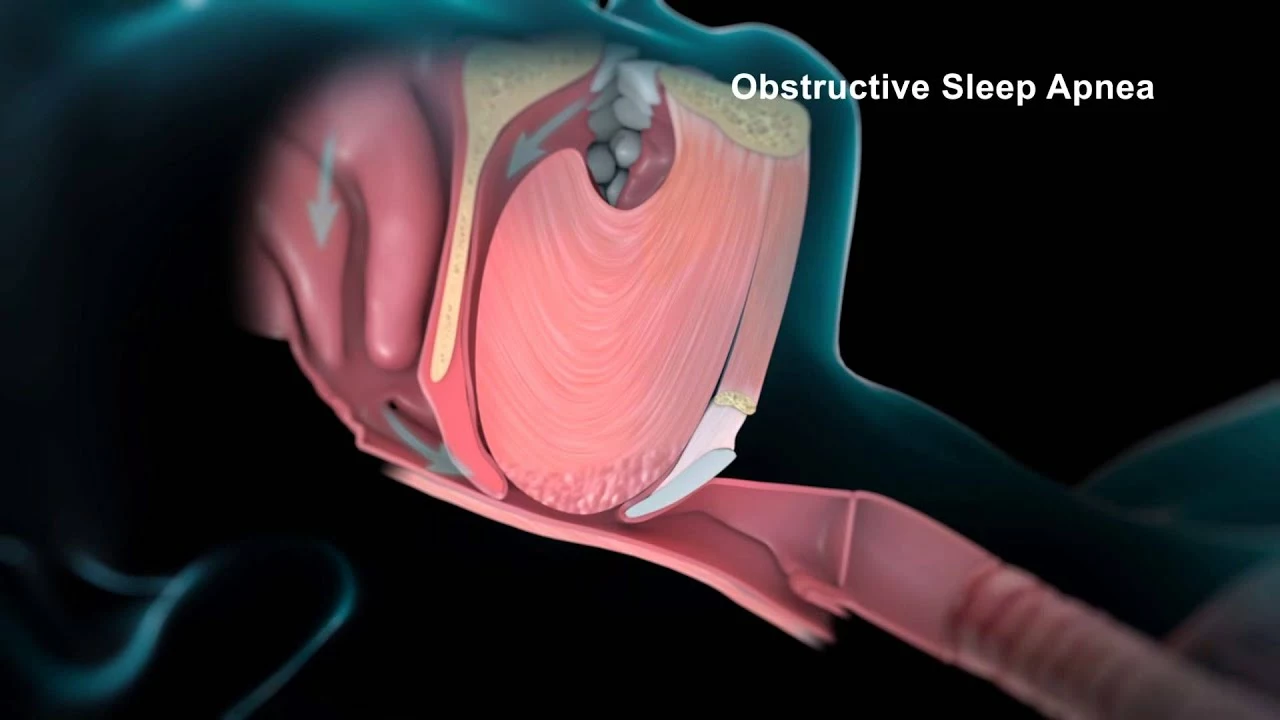
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions can lead to a variety of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. In this article, we will explore the connection between sleep apnea and blood clots in stents, a potentially dangerous complication that can occur in individuals who have undergone procedures to open blocked arteries. We will discuss the risk factors, potential consequences, and steps you can take to mitigate these risks.
What Are Stents and Why Are They Used?
Stents are small, flexible mesh tubes that are inserted into arteries to help keep them open and improve blood flow. They are often used to treat individuals with coronary artery disease, a condition in which the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. Stents can be life-saving for individuals experiencing a heart attack or those with severely blocked arteries, as they help restore blood flow and reduce the risk of further complications.
The Risk of Blood Clots in Stents
While stents can be highly effective in improving blood flow, they also carry a risk of blood clot formation. Blood clots can form on the stent itself or in the artery where the stent is placed. If a blood clot forms and blocks blood flow, it can lead to a heart attack, stroke, or other serious complications. To reduce the risk of blood clots, individuals with stents are often prescribed blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or clopidogrel.
The Connection Between Sleep Apnea and Blood Clots in Stents
Recent research has suggested a link between sleep apnea and an increased risk of blood clot formation in stents. Sleep apnea can cause fluctuations in blood oxygen levels, which can lead to inflammation and an increased risk of blood clotting. Additionally, sleep apnea is associated with other risk factors for blood clots, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
How Sleep Apnea Can Affect Blood-Thinning Medications
Individuals with sleep apnea may also be at a higher risk of blood clots in stents due to the potential impact of the condition on the effectiveness of blood-thinning medications. Sleep apnea can cause disruptions in the body's natural clotting process, which may make blood-thinning medications less effective in some individuals. This can increase the risk of blood clot formation and related complications.
Diagnosing Sleep Apnea in Individuals with Stents
Given the potential connection between sleep apnea and blood clots in stents, it is important for individuals with stents to be aware of the signs and symptoms of sleep apnea. Common symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. If you have a stent and suspect you may have sleep apnea, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Treating Sleep Apnea to Reduce the Risk of Blood Clots in Stents
If you have been diagnosed with sleep apnea and have a stent, it is crucial to seek treatment to reduce your risk of blood clot formation. Treatment options for sleep apnea include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol, as well as the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, which helps maintain an open airway during sleep.
Monitoring Blood-Thinning Medication Effectiveness
In addition to treating sleep apnea, it is also important to monitor the effectiveness of your blood-thinning medications if you have a stent. Your healthcare provider may need to adjust your medication regimen to ensure optimal blood clot prevention. Regular follow-up appointments and blood tests can help ensure that your medications are working as intended and that your risk of blood clot formation is minimized.
Conclusion: The Importance of Addressing Sleep Apnea in Individuals with Stents
In conclusion, the connection between sleep apnea and blood clots in stents highlights the importance of recognizing and addressing sleep apnea in individuals with stents. By seeking proper diagnosis and treatment for sleep apnea, monitoring the effectiveness of blood-thinning medications, and making lifestyle changes, individuals with stents can reduce their risk of blood clot formation and related complications. If you have a stent and suspect you may have sleep apnea, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your concerns and develop a comprehensive treatment plan.

Sleep apnea isn’t just about snoring; the intermittent hypoxia can trigger systemic inflammation, which in turn ramps up platelet activation. When you have a stent, that extra platelet activity can make the metal scaffold a breeding ground for thrombus. The literature shows a clear uptick in in‑stent restenosis among patients with untreated sleep‑disordered breathing. Managing the airway – whether with CPAP or lifestyle tweaks – can thus be a silent guardian for your coronary work. Keep an eye on your O₂ saturation, and talk to your cardiologist about a coordinated care plan.
The pathophysiological cascade, beginning with nocturnal hypoxemia, precipitates endothelial dysfunction; consequently, the pro‑thrombotic milieu intensifies, especially in the presence of a foreign body such as a stent. Moreover, pharmacokinetic variability of antiplatelet agents, induced by intermittent hypercapnia, may diminish therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, clinicians ought to consider polysomnographic screening for all post‑stent patients. In practice, this translates to a multidisciplinary approach-cardiology, pulmonology, and, when appropriate, sleep medicine-collaborating to mitigate clot risk. The evidence, albeit emergent, is compelling enough to warrant protocol revisions.
Sleep apnea can really mess with stent outcomes.
India has long grappled with cardiovascular disease, yet the hidden danger of untreated sleep apnea remains grossly underestimated.
When a patient with a coronary stent also suffers from obstructive sleep apnea, the intermittent oxygen desaturation triggers a cascade of inflammatory cytokines.
These cytokines, primarily interleukin‑6 and tumor necrosis factor‑alpha, destabilize the endothelium lining the stent.
Endothelial dysfunction, in turn, accelerates platelet aggregation on the metallic scaffold.
The result is a higher propensity for in‑stent thrombosis, which can precipitate myocardial infarction or stroke.
Our own clinical data from tertiary centers in Delhi and Mumbai confirm a three‑fold increase in clot formation among apnea‑positive patients.
Moreover, the standard antiplatelet regimen-aspirin plus clopidogrel-often fails to achieve adequate platelet inhibition in this subgroup.
This failure is partly due to the altered pharmacodynamics caused by fluctuating blood pH during apnea episodes.
Consequently, many patients experience subtherapeutic drug levels despite adherence to prescribed dosages.
The solution, therefore, is not merely to prescribe more antiplatelet agents but to address the root cause: the sleep disorder.
Implementing continuous positive airway pressure therapy has been shown to normalize inflammatory markers within weeks.
In addition, weight reduction, alcohol moderation, and positional therapy further diminish apnea severity.
Clinicians should mandate a sleep study for any post‑stent patient presenting with snoring, nocturnal gasps, or daytime fatigue.
Healthcare policymakers must allocate resources to make polysomnography accessible, especially in rural areas where cardiovascular morbidity is rising.
Only by integrating sleep medicine into cardiology can we truly curb the tide of stent‑related thrombotic events in our nation.
Wow that was a thorough breakdown, and I love how you tied together the data from our local hospitals with actionable steps. First, getting a sleep study done is something we can all push for at our next check‑up. Second, using CPAP consistently can actually lower the inflammation you mentioned and keep the stent clear. Third, staying active and watching our diet helps both blood pressure and apnea severity. I’ve seen friends who added just a few minutes of walking each day and noticed they slept better too. It’s amazing how small lifestyle tweaks can have a ripple effect on heart health. Keep spreading the word, because the more people know, the more we can prevent those scary clot events.
Seriously you should all just stop ignoring your health. If you don’t get treated for sleep apnea you’re basically asking for trouble. It’s not okay to risk a heart attack because you’re lazy. Do the sleep test, wear the mask, and eat right. No excuses.
While the moral imperative is clear, one must also appreciate the nuanced interplay of physiological and sociopolitical factors, lest we reduce a complex condition to mere laziness; indeed, the Western emphasis on quick fixes overlooks the holistic approach required for genuine cardiovascular resilience.