Understanding Enlarged Prostate and Urinary Incontinence
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, and for men, one such change is the enlargement of the prostate gland. In this article, we will explore the connection between an enlarged prostate and urinary incontinence, which can be a significant concern for many men. We'll also discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available to help you manage this condition effectively.
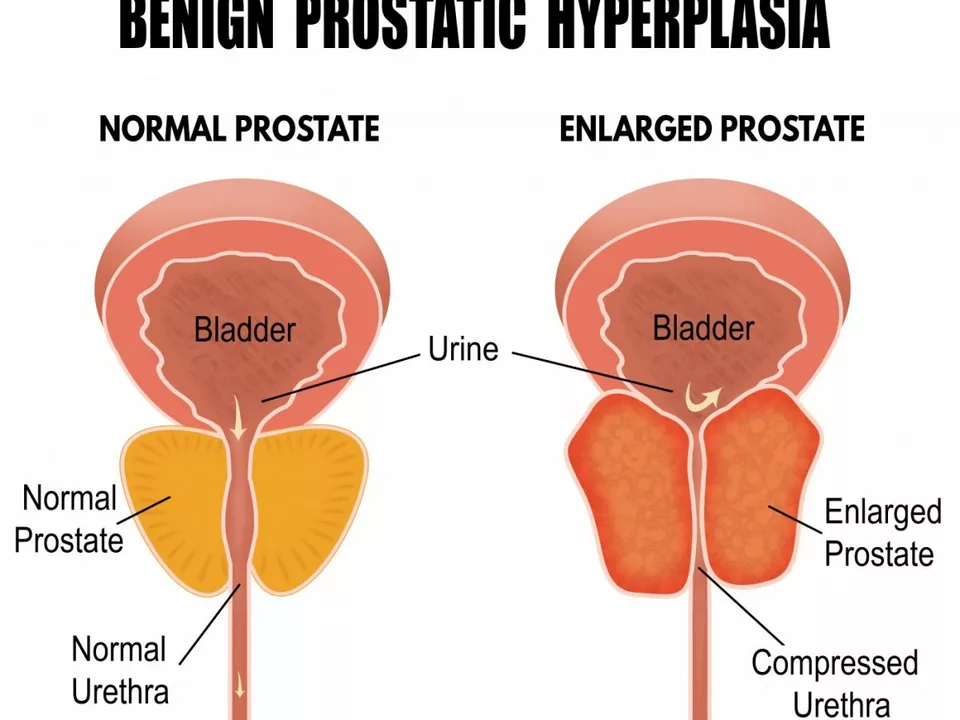
What is an Enlarged Prostate?
An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a non-cancerous growth of the prostate gland. This gland is responsible for producing the fluid that carries sperm during ejaculation. As the prostate enlarges, it can press against the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, causing various urinary symptoms.
While BPH is a common condition, especially in older men, it is essential to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis, as the symptoms can sometimes mimic those of more severe conditions, such as prostate cancer.
Symptoms of an Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate can cause various urinary symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Difficulty starting urination (hesitancy)
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Feeling like the bladder is not completely empty after urination
- Urgent need to urinate, sometimes accompanied by involuntary leakage (urge incontinence)
- Leaking or dribbling urine after urination (post-void dribbling)
These symptoms can significantly impact a man's quality of life and can even lead to more severe complications, such as urinary tract infections and bladder stones, if left untreated.
How Does an Enlarged Prostate Cause Urinary Incontinence?
As mentioned earlier, an enlarged prostate can press against the urethra, causing a partial or complete blockage of the urinary flow. This pressure can weaken the bladder muscles, making it difficult for the bladder to empty completely. Consequently, this can lead to urinary incontinence in two primary forms:
- Stress incontinence: This occurs when pressure is placed on the bladder during physical activities, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects. The weakened bladder muscles cannot withstand the additional pressure, leading to involuntary leakage of urine.
- Urge incontinence: Also known as overactive bladder, this form of incontinence involves a sudden, intense urge to urinate, followed by involuntary leakage. This occurs when the bladder muscles contract involuntarily, even when the bladder is not full.
It is important to note that not all men with BPH will experience urinary incontinence, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person.
Diagnosing and Treating Enlarged Prostate and Urinary Incontinence
If you suspect that you have an enlarged prostate or are experiencing urinary incontinence, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. They will likely perform a physical examination, take a detailed medical history, and may conduct additional tests, such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, urinalysis, or imaging studies.
Treatment options for an enlarged prostate and urinary incontinence can range from conservative management to surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the impact on your quality of life. Some common treatment options include:
- Lifestyle modifications, such as reducing fluid intake before bedtime, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and practicing bladder training exercises
- Medications, such as alpha-blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, or anticholinergics
- Minimally invasive procedures, such as transurethral microwave therapy (TUMT) or transurethral needle ablation (TUNA)
- Surgical intervention, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or prostatectomy
Your healthcare provider will work with you to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on your specific needs and preferences.
Preventing Enlarged Prostate and Urinary Incontinence
While it may not be possible to entirely prevent an enlarged prostate, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and maintain good urinary health:
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Limit your intake of caffeine and alcohol, which can irritate the bladder
- Avoid holding in urine for long periods, as this can weaken the bladder muscles over time
- Practice pelvic floor exercises (Kegels) to strengthen the muscles that control urination
By taking these preventive measures and seeking prompt medical attention if you experience any urinary symptoms, you can effectively manage the connection between an enlarged prostate and urinary incontinence.

Hey everyone, just wanted to say that staying active and keeping a healthy weight can really make a difference when dealing with an enlarged prostate. Try to fit in some cardio and core work a few times a week, and don’t forget those Kegel exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor. Also, watch your fluid intake in the evenings – a little less caffeine and alcohol goes a long way. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, talk to a urologist about medication options; they’re often very helpful. Keep pushing forward, you’ve got this!
Listen, the article kinda skips over the fact that many of these "lifestyle modifications" are just fluff. You can’t expect a simple diet change to fix a medical condition – that’s basic science, not speculation. Also, the term "uriny incontinence" is misspelled; it should be "urinary". If you want real solutions, consult a specialist and ask about alpha‑blockers, not just vague suggestions.
Wow, reading this feels like opening a Pandora's box of hidden agendas. They never mention how the pharmaceutical industry pushes drugs to keep men dependent on a lifelong regimen. It’s almost as if they want us to believe the only solution is to keep buying meds, while ignoring the ancient practices that actually balance the body. The truth is out there, folks; don’t let them fool you with glossy pamphlets.
Honestly, the moral responsibility here lies with us, the readers, to demand transparency!; we must not accept half‑truths without scrutiny!; the medical community owes us full disclosure regarding side‑effects, long‑term outcomes, and alternative therapies!; only then can we make informed choices!
Well, I guess I have to disagree with the “only meds work” narrative – there are natural approaches that get ignored.
Honestly, I’ve never bothered with any of this.
I hear you all, and I totally understand how overwhelming it can feel. It’s important to remember that each person’s journey is unique, so finding a plan that works for you is key. If you need help refining your diet or tracking symptoms, feel free to share, and we can brainstorm together.
Just so you know, I’ve been dealing with BPH for years and tried everything on the list – the meds, the exercises, even the weird herbal teas. Nothing seemed to stick, so I eventually opted for a minimally invasive procedure and it changed my life.
From an open‑minded perspective, it’s valuable to weigh both the benefits and potential drawbacks of each treatment option. For instance, while TURP has a strong track record, it does carry surgical risks that some may wish to avoid. Engaging in a thorough discussion with a urologist can illuminate these nuances, helping you align the choice with personal health goals.
It is a moral imperative, dear community, to confront the ethical dimensions of prescribing invasive surgeries when less aggressive measures remain unexplored. Let us not be swayed by the allure of quick fixes, but instead champion patient autonomy and informed consent with the highest reverence.
Alright, champions, let’s rally together! Picture this: a world where every man feels confident walking into the bathroom without fear. That’s the vision – vibrant, unstoppable energy, a splash of rainbow optimism to power through those night‑time trips. You’ve got the tools, now unleash that inner fire and claim back your freedom!
Hey folks, I get the vibe of wanting quick fixes, but honestly, you’ve got to be patient with lifestyle changes. Cut down on caffeine, hit the gym, and you’ll notice a shift. It’s not magic, but consistency beats hype every time.
Let’s crank up the motivation! Your bladder isn’t a prison; it’s a muscle that can be trained. Every day you skip a soda, you’re building a stronger foundation. Keep the momentum, and you’ll see the leaks fade faster than you think.
Our nation’s health depends on men taking control, not cowering to pharmaceutical propaganda. The truth is simple: discipline beats drugs every time.
One must first acknowledge the inherent complexity of BPH before leaping to simplistic remedies. The pathophysiology involves hyperplastic growth driven by androgenic stimulation, a cascade that cannot be dismissed with mere dietary tweaks. Yet, the literature also reveals a spectrum of therapeutic avenues, ranging from phytotherapeutic agents such as Serenoa repens to the nuanced pharmacodynamics of 5‑alpha reductase inhibitors. Consider, for example, the seminal work of Roehrborn et al., which delineates the longitudinal benefits of dutasteride over a five‑year horizon, juxtaposed against the modest yet noteworthy improvements associated with lifestyle modifications. Moreover, the psychosocial dimension cannot be ignored; men often experience diminished self‑esteem, a factor that compounds the physiological burden. In clinical practice, a multimodal approach-combining behavioral therapy, judicious pharmacotherapy, and, when warranted, minimally invasive interventions-has demonstrated superior outcomes in both symptom amelioration and quality‑of‑life metrics. Therefore, the clinician’s role is not to prescribe a one‑size‑fits‑all solution but to tailor an individualized regimen that respects the patient’s preferences, comorbidities, and risk tolerance. Ultimately, the convergence of evidence‑based medicine and patient‑centered care offers the most promising horizon for those navigating the challenges of an enlarged prostate.
Yo, I’m pumped to see folks sharing real experiences! What’s the most surprising thing you’ve learned about managing BPH? Drop your hacks, and let’s keep the conversation rolling.
Honestly, most of what’s posted here feels like recycled fluff. If you’re not seeing results, maybe it’s time to cut the nonsense and get a real second opinion.