Understanding the Link Between Hormones and Infections
As a woman, I've often wondered why I seem to be more prone to certain infections at different times of my menstrual cycle. After doing some research, I discovered that hormonal changes can actually trigger intestinal and vaginal infections. In this article, I'm going to share what I've learned about the connection between hormones and infections, and how we can manage these changes to maintain our overall health.
The Role of Hormones in Our Bodies
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various processes in our bodies, including our reproductive systems. They are responsible for controlling the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, menopause, and more. The two primary female hormones - estrogen and progesterone - can significantly affect our gut and vaginal health. When the levels of these hormones fluctuate, it can create an environment that promotes the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to infections.
How Hormonal Fluctuations Impact Gut Health
Our gut health is closely linked to our overall well-being, as it plays a vital role in digestion, immune function, and even mental health. When hormonal fluctuations occur, it can disrupt the balance of good and bad bacteria in our intestines, leading to a variety of gastrointestinal issues. For example, higher levels of estrogen can slow down digestion and cause constipation, while lower levels can lead to diarrhea. This imbalance can also make us more susceptible to infections, such as bacterial overgrowth and yeast infections.
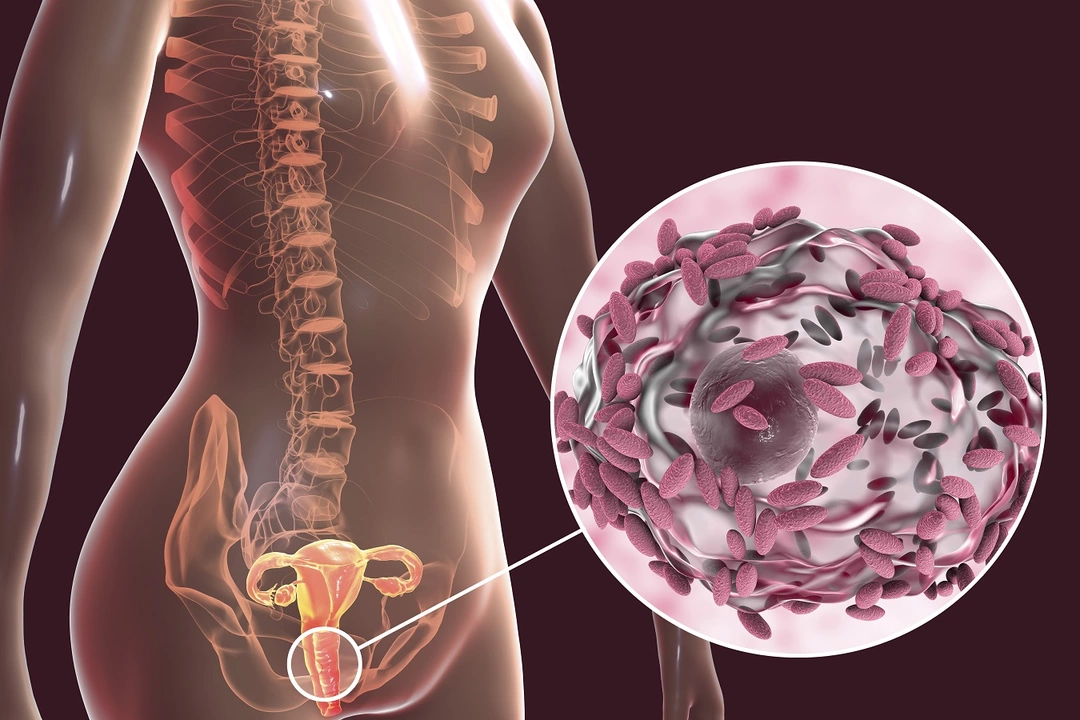
Hormonal Changes and Vaginal Infections
Just like in our gut, hormonal fluctuations can also impact the balance of bacteria in our vaginal area. When estrogen levels are high, it supports the growth of lactobacilli, which are beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy vaginal pH. However, when hormone levels drop, it can create an environment that favors the growth of harmful bacteria, such as yeast and other pathogens, leading to infections like bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections.
Menstrual Cycle and Infection Risk
Many women, including myself, have noticed that we tend to experience more gastrointestinal and vaginal issues during certain phases of our menstrual cycle. This is because our hormone levels fluctuate throughout the month, with estrogen and progesterone levels peaking around ovulation and then declining before menstruation. These fluctuations can create an environment that is more conducive to infections, making us more susceptible to developing issues like yeast infections and bacterial overgrowth.
Managing Hormonal Fluctuations to Prevent Infections
While we can't completely control our hormonal fluctuations, there are some steps we can take to help minimize their impact on our gut and vaginal health. One of the most important things we can do is to maintain a healthy lifestyle, which includes eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress. In addition, taking probiotics can help support the growth of beneficial bacteria in our gut and vagina, which can help to prevent infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While hormonal fluctuations are a normal part of a woman's life, it's important to pay attention to our bodies and seek medical attention if we suspect that we may have an infection. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, changes in bowel habits, vaginal itching, and unusual discharge can all be signs of an infection. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
In conclusion, understanding the link between hormonal changes and intestinal and vaginal infections can help us take better care of our bodies and maintain our overall health. By being aware of these connections and taking steps to manage our hormonal fluctuations, we can reduce the risk of developing infections and maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in our gut and vaginal area.

I've been thinking about how those hormone swings we all go through can feel like a roller coaster for our bodies, especially when it comes to the gut and down there. When estrogen peaks around ovulation, you might notice a slower digestion, which can leave you feeling bloated and even constipated. Then, just as quickly, when progesterone drops before your period, things can speed up and you might end up with a runny tummy. That kind of back‑and‑forth can throw off the delicate balance of good bacteria that keep infections at bay.
On top of that, the vaginal environment is like a tiny ecosystem that thrives on a stable pH, and hormones are the weathermen. High estrogen supports lactobacilli, the good guys that keep nasty microbes in check, while a dip can give opportunistic yeast a chance to flourish. The result? More frequent yeast infections or bacterial vaginosis at certain points in the cycle.
What helps me stay ahead of the game is a combo of diet, movement, and a little probiotic boost. Fermented foods like kefir or a daily supplement can seed both the gut and the vagina with helpful microbes. Also, staying hydrated, moving your body regularly, and managing stress are like the under‑the‑hood maintenance that keeps the whole system running smooth.
Bottom line: you don’t have to feel trapped by your hormones. By paying attention to the signs, supporting your microbiome, and not ignoring persistent symptoms, you can keep those infections in check and feel more balanced throughout the month.
I totally get how frustrating it can be when your body seems to fight you during certain phases of the cycle. Keeping a simple food diary can really show patterns, like more sugar cravings when estrogen drops, which can feed yeast. Adding a daily probiotic with strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus can help keep both gut and vaginal flora balanced. Also, staying active, even a short walk, supports digestion and reduces stress, which in turn calms hormone spikes. Just listen to your body and give it the gentle care it needs.
Honestly, I think the whole hormone‑infection link is a bit overblown. Sure, hormones fluctuate, but most infections are caused by hygiene or diet, not some mystical hormonal drama. People love to blame their cycle for everything, from acne to a slight tummy upset, when the real culprit could be sugar overload or antibiotic use. If you focus too much on hormones, you might miss the simple fixes like cleaning up your diet or swapping out that scented feminine wash.
While the hormonal influence is undeniable, it is also important to consider the role of the immune system in this interplay. Estrogen tends to enhance certain immune responses, whereas progesterone can suppress them, creating windows of vulnerability. A balanced diet rich in fiber and polyphenols supports the gut‑associated lymphoid tissue, which in turn can fortify mucosal defenses. Moreover, regular moderate exercise has been shown to modulate hormone levels subtly, reducing extreme peaks that may destabilize microbial ecosystems.
The article oversimplifies a complex issue. While hormones do affect microbial balances, attributing infections solely to hormonal swings ignores other critical factors such as antibiotic exposure, sexual health practices, and underlying chronic conditions. Readers should be cautious about adopting a one‑size‑fits‑all approach and instead seek personalized medical advice.
Consider using a probiotic containing multiple Lactobacillus strains for better colonisation.
I love how the post ties hormone cycles to both gut and vaginal health, showing how interconnected our bodies truly are. It reminds me that everything from what we eat to how we manage stress can influence that delicate microbial balance. When estrogen rises, the increase in glycogen can feed beneficial lactobacilli, yet when it drops, those same microbes can lose their foothold, making way for opportunistic pathogens. The same principle applies in the gut; estrogen can slow motility, leading to constipation, which gives harmful bacteria a chance to proliferate.
What stands out is the practicality of the suggestions – balanced nutrition, regular movement, stress reduction, and targeted probiotic use. These steps are accessible and empower us to take charge of our health rather than feeling at the mercy of our cycles. Consistency is key, and paying attention to subtle changes can prevent bigger issues later.